iOS In-App Automation Customization
Import In-App Automation
In-app messaging services are available as part of the Airship framework as well as a standalone framework called AirshipAutomation.
To access the in-app messaging from the Airship framework, simply import Airship where necessary.
"Plists can be used to modify any of the default"
import AirshipKitTo access in-app messaging from the AirshipAutomation standalone framework, you must add a separate import statement in your code, as shown below:
import AirshipAutomationDisplay Delegate
A delegate can be added to the in-app messaging manager to listen for when a message is displayed, finished displaying, and to control when a message is displayed. This is useful for adding analytics events outside of Airship as well as for further processing of the in-app message.
func isMessageReadyToDisplay(_ message: InAppMessage, scheduleID: String) -> Bool {
/// Used to control if the message is ready to display if you return false here it wont display.
/// Use `InAppAutomation.shared.inAppMessaging.notifyDisplayConditionsChanged()` to notify Airship when
/// it should check again.
return true
}
func messageWillDisplay(_ message: InAppMessage, scheduleID: String) {
/// Called before the message is displayed
}
func messageFinishedDisplaying(_ message: InAppMessage, scheduleID: String) {
/// Called after the message is displayed
}// Setting the delegate
InAppAutomation.shared.inAppMessaging.displayDelegate = displayDelegate;Scene Delegate
The InAppMessageSceneDelegate facilitates overriding the UIWindowScene on which a given in-app message is displayed.
func sceneForMessage(_ message: InAppMessage) -> UIWindowScene? {
// return a custom scene or nil to use default
}InAppAutomation.shared.inAppMessaging.sceneDelegate = sceneDelegateFonts
Custom Fonts
Fonts added to the app bundle are available for use with in-app messaging. To add
fonts, please read the The UIKit Custom Fonts Guide .
After adding fonts to your app, create a Font Stack in the Airship dashboard by following the steps in our Custom fonts guide.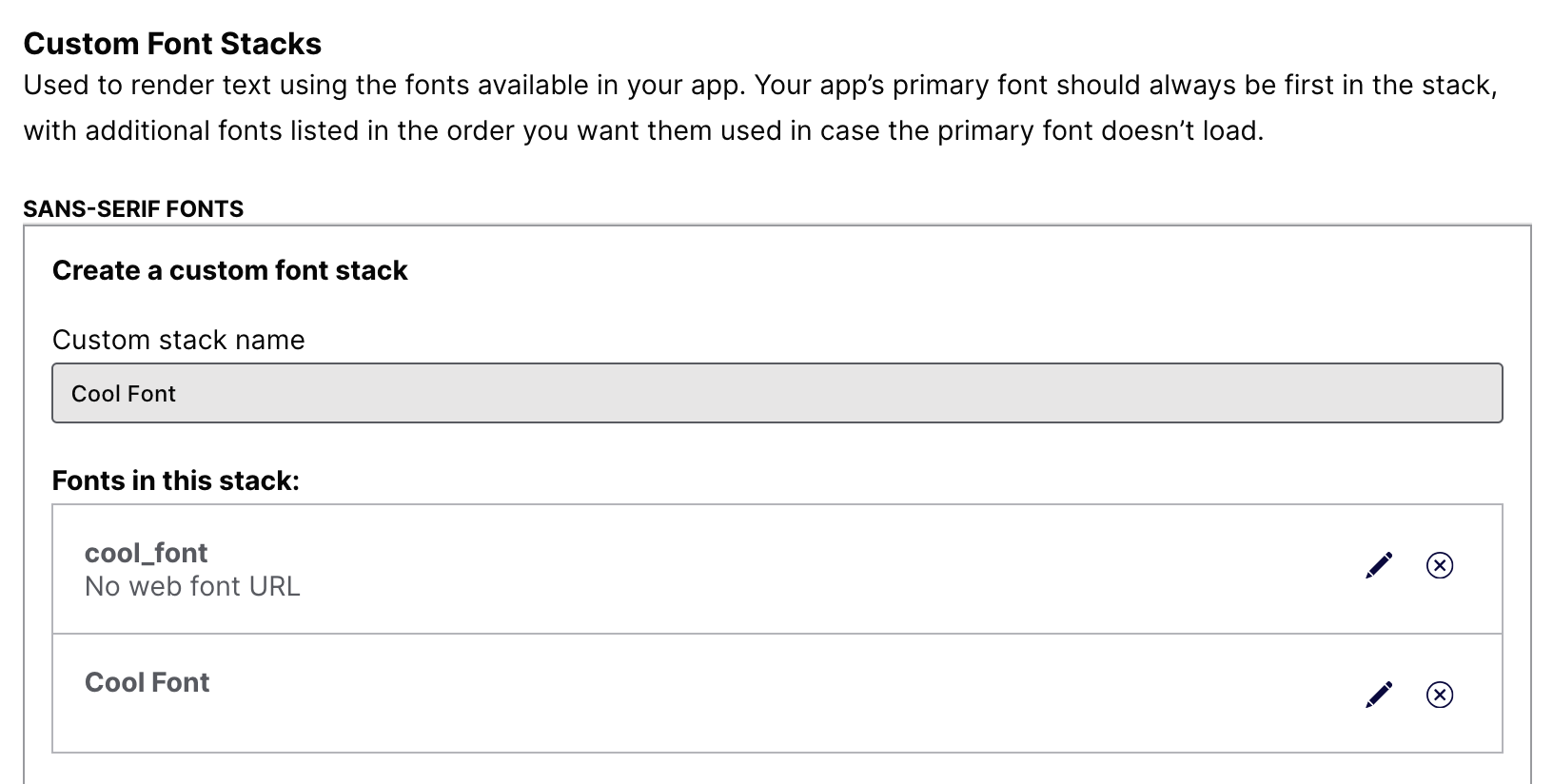
Then you can select the stack when setting in-app message defaults and creating in-app messages.
Dynamic fonts With HTML in-app messages
Most In-App message styles support automatically scaling fonts through the use of Dynamic Type. However, automatically scaling fonts in HTML In-App messages requires you to use the following Apple system fonts when specifying the CSS font property:
-apple-system-body-apple-system-headline-apple-system-subheadline-apple-system-caption1-apple-system-caption2-apple-system-footnote-apple-system-short-body-apple-system-short-headline-apple-system-short-subheadline-apple-system-short-caption1-apple-system-short-footnote-apple-system-tall-body
For example, to have the HTML body default to the Apple system font body style:
body {
font: -apple-system-body; // available on Apple devices only
}For more information about dynamic type, please see this WWDC video .
Styles
Plists can be used to modify any of the default message styles that the SDK provides. Each message type can be customized with a different plist:
- Banner:
UAInAppMessageBannerStyle.plist - HTML:
UAInAppMessageHTMLStyle.plist - FullScreen:
UAInAppMessageFullScreenStyle.plist - Modal:
UAInAppMessageModalStyle.plist
Plist values:
Banner
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the view.headerStyle: Text Style. Customizes the message’s header.bodyStyle: Text Style. Customizes the message’s body.mediaStyle: Media Style. Customizes the message’s media.buttonStyle: Buttons Style. Customizes the message’s buttons.maxWidth: Points. Max width.tapOpacity: Tap Opacity. Customizes the message’s opacity it’s tapped and a tap action is present.shadowStyle: Shadow Style. Customizes the message’s shadow.
FullScreen
headerStyle: Text Style. Customizes the banner’s header.bodyStyle: Text Style. Customizes the banner’s body.mediaStyle: Media Style. Customizes the banner’s media.buttonStyle: Buttons Style. Customizes the banner’s buttons.dismissIconResource: String. Resource name for a custom dismiss icon.
Modal
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the view.headerStyle: Text Style. Customizes the banner’s header.bodyStyle: Text Style. Customizes the banner’s body.mediaStyle: Media Style. Customizes the banner’s media.buttonStyle: Buttons Style. Customizes the banner’s buttons.dismissIconResource: String. Resource name for a custom dismiss icon.maxWidth: Points. Max width.maxHeight: Points. Max height.extendFullScreenLargeDevice: Boolean. True to allow the option ‘Display fullscreen on small screen device’ to extend to large devices as well.
HTML
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the view.dismissIconResource: String. Resource name for a custom dismiss icon.maxWidth: Points. Max width.maxHeight: Points. Max height.extendFullScreenLargeDevice: Boolean. True to allow the option ‘Display fullscreen on small screen device’ to extend to large devices as well.
Padding
top: Points. Top padding.bottom: Points. Bottom padding.leading: Points. Leading padding.trailing: Points. Trailing padding.
Buttons Style
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the button area.buttonHeight: Points. Button height.stackedButtonSpacing: Points. Button spacing in the stacked layout.separatedButtonSpacing: Points. Button spacing in the separated layout.borderWidth: Points. Button’s border width.buttonTextStyle: Text Style. Text style for each button.
Text Style
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the view.letterSpacing: Points. Spacing between the letters.lineSpacing: Points. Spacing between lines.
Media Style
additionalPadding: Padding. Adds padding around the view.
Shadow Style
colorHex: Color. Shadow color.radius: Points. Shadow radius.xOffset: Points. Shadow x-axis offset.yOffset: Points. Shadow y-axis offset.
Custom adapters
Providing an adapter allows defining the behavior of the custom type or overriding any of the default message types. The adapter will be created by the in-app messaging manager when a message’s schedule is triggered. Once created, the adapter can define when the message is ready to display and the display behavior.
After the message is displayed, the caller of the display method must be notified
that the message is finished displaying by returning a CustomDisplayResolution when
finished. This will allow for subsequent in-app messages to be displayed.
final class CustomBannerAdapter: CustomDisplayAdapter {
private let message: InAppMessage
private let assets: AirshipCachedAssetsProtocol
init(message: InAppMessage, assets: any AirshipCachedAssetsProtocol) {
self.message = message
self.assets = assets
}
@MainActor
var isReady: Bool {
get {
/// Called before display
return true
}
}
@MainActor
func waitForReady() async {
// If `isReady` is false this will be called to wait for the
// adapter to be ready
}
@MainActor
func display(scene: UIWindowScene) async -> CustomDisplayResolution {
return await withCheckedContinuation { continuation in
/// After displaying call the continuation with the result
continuation.resume(returning: .userDismissed)
}
}
}/// Set the factory block after takeOff
InAppAutomation.shared.inAppMessaging.setAdapterFactoryBlock(forType: .banner) { message, assets in
return CustomBannerAdapter(message: message, assets: assets)
}Standard In-App Messages
Standard in-app messages delivered through push messages are managed by the legacy in-app message manager. Apps can provide extender blocks to modify the message and/or schedule when an in-app message is converted to a banner.
InAppAutomation.shared.legacyInAppMessaging.scheduleExtender = { schedule in
// Modify the schedule
schedule.limit = 2
}InAppAutomation.shared.legacyInAppMessaging.messageExtender = { message in
/// Modify the message
if case .banner(var bannerInfo) = message.displayContent {
bannerInfo.borderRadius = 10.0
message.displayContent = .banner(bannerInfo)
}
}Customizing HTML In-App Messages
In order for the Airship JavaScript interface to be loaded into the webview, the URL must be specified in the URL Allowlist.
HTML in-app messages provide a way to display custom content inside a native web view. These types of in-app messages display with a dismiss button built in, but can also be customized to provide their own buttons capable of dismissing the view. Dismissing a view requires calling the dismiss function on the UAirship JavaScript interface with a button resolution object passed in as a parameter. The button resolution object is a JSON object containing information about the interaction type and the button performing the dismissal. It should match the following format:
{
"type" : "button_click",
"button_info" : {
"id" : "button identifier",
"label" : {"text": "foo"}
}
}The button resolution requires each of the key fields shown above. These include:
type— The type key with the value of resolution typebutton_clickbutton_info— The button info object containing required id and label fieldsid— The button identifierlabel— Label object containing the required text keytext— The text key with a string value representing the label text
Providing a basic dismiss button in HTML:
<button onclick="UAirship.dismiss({
'type' : 'button_click',
'button_info' : {
'id' : 'button identifier',
'label' : {'text' : 'foo'}
}
}
);">Dismiss with resolution</button>Categories
