Install & Setup the Apple SDK
Learn how to install the Airship SDK using SPM, CocoaPods, Carthage, or xcframeworks, and initialize the SDK in your iOS, tvOS, or visionOS applications.
The Airship SDK is a modern, Swift 6-native SDK designed for Apple platforms. It provides type-safe, actor-isolated APIs with full Swift concurrency support that work seamlessly across iOS, tvOS, and visionOS — all from a single SDK.
For a complete reference of feature support across iOS, tvOS, and visionOS, see Platform Support.
Requirements
- Minimum iOS version: 16.0+
- Minimum tvOS version: 18.0+
- Minimum visionOS version: 1.0+
- Requires Xcode 26.0+
SDK installation
The Airship SDK can be installed using SPM (Swift Package Manager), CocoaPods, Carthage, or xcframeworks. We recommend SPM for new projects.
Install Airship
In your Xcode project, select your project in the Project Navigator.
Select your target, then go to the Package Dependencies tab.
Click the + button to add a package.
Enter the package URL:
https://github.com/urbanairship/ios-librarySelect the version rule (recommended: “Up to Next Major Version”).
Click Add Package.
Select the Airship package products you want to include in your app:
Available package products:
AirshipBasement: Required by AirshipCoreAirshipCore: Push messaging features including channels, tags, named user and default actions (required)AirshipMessageCenter: Message centerAirshipAutomation: Automation and in-app messagingAirshipPreferenceCenter: Preference CenterAirshipFeatureFlags: Feature FlagsAirshipObjectiveC: Objective-C BindingsAirshipDebug: Debugging toolsAirshipNotificationServiceExtension: Service Extension framework (only for Notification Service Extension targets, not the app target)*
Click Add Package.
Import the modules in your code where needed. Import statements match the module names:
import AirshipCore
import AirshipMessageCenter
import AirshipAutomationFor more details, see Apple’s guide on adding package dependencies to your app.
CocoaPods trunk is moving to read-only mode in December 2026. Airship will continue to support CocoaPods as long as possible, but we recommend using SPM (Swift Package Manager) for new projects. Existing CocoaPods installations will continue to work after trunk becomes read-only.
- Install CocoaPods if you haven’t already:
$ gem install cocoapodsNavigate to your project directory in Terminal.
Create a
Podfile(if one doesn’t exist):
$ pod init- Open your
Podfileand add the Airship pod. TheAirshippod is modular and divided into subspecs:
Available subspecs:
Airship/Core: Push messaging features including channels, tags, named user and default actions (required)Airship/MessageCenter: Message centerAirship/Automation: Automation and in-app messagingAirship/PreferenceCenter: Preference Center moduleAirship/FeatureFlags: Feature Flags moduleAirship/ObjectiveC: Objective-C bindings
target "<Your Target Name>" do
pod 'Airship'
endOr specify individual subspecs:
target "<Your Target Name>" do
pod 'Airship/Core'
pod 'Airship/MessageCenter'
pod 'Airship/Automation'
pod 'Airship/FeatureFlags'
endFor tvOS projects, specify the platform:
platform :tvos, '18.0'
target "<Your Target Name>" do
pod 'Airship'
end- Install the pods:
$ pod install- Important: After running
pod install, an Xcode workspace (.xcworkspace) file is generated. Always open the workspace file instead of the project file (.xcodeproj) when building your project.
If you encounter issues, see the CocoaPods troubleshooting guide.
Install Carthage if you haven’t already. See the Carthage installation guide.
Verify
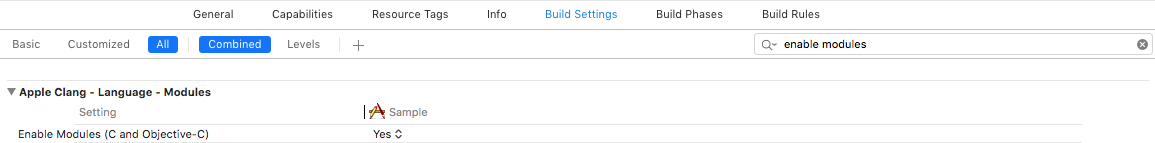
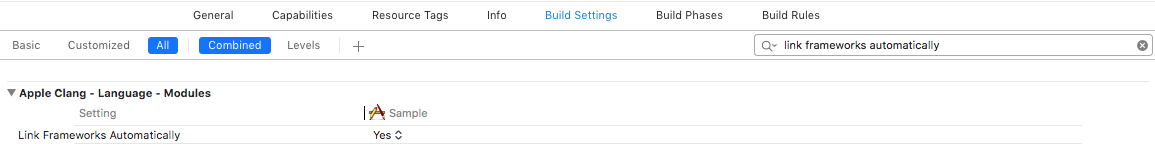
Enable ModulesandLink Frameworks Automaticallyare enabled in your project’s Build Settings.Follow Carthage’s adding frameworks to an application instructions to add frameworks to your application.
Specify the Airship iOS SDK in your
Cartfile:
github "urbanairship/ios-library"- Build the frameworks:
$ carthage updateAdd the frameworks to your project. Airship is modular, so select only the frameworks you need:
Available frameworks:
AirshipBasement: Required by AirshipCoreAirshipCore: Push messaging features including channels, tags, named user and default actions (required)AirshipMessageCenter: Message centerAirshipAutomation: Automation and in-app messagingAirshipPreferenceCenter: Preference CenterAirshipFeatureFlags: Feature FlagsAirshipObjectiveC: Objective-C BindingsAirshipDebug: Debugging toolsAirshipNotificationServiceExtension: Service Extension framework (only for Notification Service Extensions)*
Import the frameworks in your code. Import statements match the framework names:
import AirshipCore
import AirshipMessageCenter
import AirshipAutomationDownload and decompress the latest version of the iOS SDK.
Inside the folder you should see a collection of XCFrameworks. Airship is modular, so select only the XCFrameworks you need:
Available XCFrameworks:
AirshipBasement.xcframework: Required by AirshipCoreAirshipCore.xcframework: Push messaging features including channels, tags, named user and default actions (required)AirshipMessageCenter.xcframework: Message centerAirshipAutomation.xcframework: Automation and in-app messagingAirshipPreferenceCenter.xcframework: Preference CenterAirshipFeatureFlags.xcframework: Feature FlagsAirshipObjectiveC.xcframework: Objective-C BindingsAirshipDebug.xcframework: Debugging toolsAirshipNotificationServiceExtension.xcframework: Service Extension framework (only for Notification Service Extensions)*
Add XCFrameworks to your project:
- Open your project in Xcode
- Click on your project in the Project Navigator
- Select your target
- Make sure the General tab is selected
- Scroll down to Frameworks, Libraries, and Embedded Content
- Drag in desired XCFrameworks from the downloaded SDK. They are wired up automatically as dependencies of your target
Verify Build Settings:
Enable Modulesshould be set toYesLink Frameworks Automaticallyshould be set toYes
- Import the frameworks in your code. Import statements match the framework names:
import AirshipCore
import AirshipMessageCenter
import AirshipAutomationInitialize Airship
The Airship SDK requires only a single entry point, known as takeOff. For UIKit apps, initialize during the application delegate’s application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:) method. For SwiftUI apps, you can initialize in the App’s init() method.
Before calling takeOff, configure the following:
App Credentials: Airship requires app credentials (app key and app secret) to authenticate your application. You can find these in the Airship dashboard under Settings → APIs & Integrations → App Keys. You need separate credentials for development and production environments.
On iOS, this is necessary because Apple provides separate APNS (Apple Push Notification Service) environments:
- Development/Sandbox: Used for testing and development builds
- Production: Used for App Store and TestFlight builds
The SDK automatically selects the correct credentials based on your build configuration. Configure both sets of credentials in your code, and use the
#if DEBUGconditional to switch between environments.Cloud Site: Airship config defaults to the US cloud site. If your application is set up for the EU site, set the site on the config options to
.eu.
Calling takeOff
The following examples show how to configure and call takeOff programmatically. Alternatively, you can configure Airship using an AirshipConfig.plist file—see Advanced Integration for details.
Call takeOff
import SwiftUI
import AirshipCore
@main
struct MyApp: App {
init() {
var config = AirshipConfig()
// Set credentials
config.productionAppKey = "YOUR PRODUCTION APP KEY"
config.productionAppSecret = "YOUR PRODUCTION APP SECRET"
config.developmentAppKey = "YOUR DEVELOPMENT APP KEY"
config.developmentAppSecret = "YOUR DEVELOPMENT APP SECRET"
// Set cloud site (.us or .eu)
config.site = .us
#if DEBUG
config.inProduction = false
config.isAirshipDebugEnabled = true
#else
config.inProduction = true
#endif
try! Airship.takeOff(config)
}
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView()
}
}
}For UIKit apps, call takeOff in your AppDelegate’s application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:) method instead of the App’s init().
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
UAConfig *config = [UAConfig config];
// Set credentials
config.productionAppKey = @"YOUR PRODUCTION APP KEY";
config.productionAppSecret = @"YOUR PRODUCTION APP SECRET";
config.developmentAppKey = @"YOUR DEVELOPMENT APP KEY";
config.developmentAppSecret = @"YOUR DEVELOPMENT APP SECRET";
// Set cloud site (UACloudSiteUS or UACloudSiteEU)
config.site = UACloudSiteUS;
#if DEBUG
config.inProduction = NO;
config.isAirshipDebugEnabled = YES;
#else
config.inProduction = YES;
#endif
NSError *airshipError;
[UAirship takeOff:config error:&airshipError];
NSAssert(airshipError == nil, @"TakeOff failed %@", airshipError);
return YES;
}
@endThe Airship SDK automatically integrates with your app by default, so you don’t need to implement push-related UIApplicationDelegate or UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate methods. This works for most applications out of the box. For advanced use cases or to disable automatic integration, see the Advanced Integration guide.
Test the integration
After completing the setup, verify your integration:
- Build and run your app in Xcode
- Check the console logs for Airship channel creation:
- Look for a log message:
Channel ID: <CHANNEL_ID> - The channel ID will be displayed in the console output
- For more detailed logging, see Logging
- Look for a log message:
If you see the channel ID in the console logs and no errors, your integration is successful. You can now proceed with configuring deep links, push notifications, and other Airship features.
If you don’t see a channel ID in the console logs or encounter errors during initialization, see the Troubleshooting guide for common problems and solutions.